01.
(문제를 잘 이해한 게 맞는지 모르겠다.)
// 책에 서술된 대로 구현
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int cnt;
void print(const string* s, int n = 0)
{
if (n == 0)
{
cnt++;
cout << "\n문자열을 한 번 출력합니다. >> ";
cout << *s << '\n';
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
cout << "\n문자열을 " << i + 1 << "번 출력합니다. >> ";
cout << *s << '\n';
}
}
}
int main()
{
string s = "abcdefg";
print(&s);
print(&s);
print(&s);
print(&s);
print(&s, 1);
return 0;
}
결과
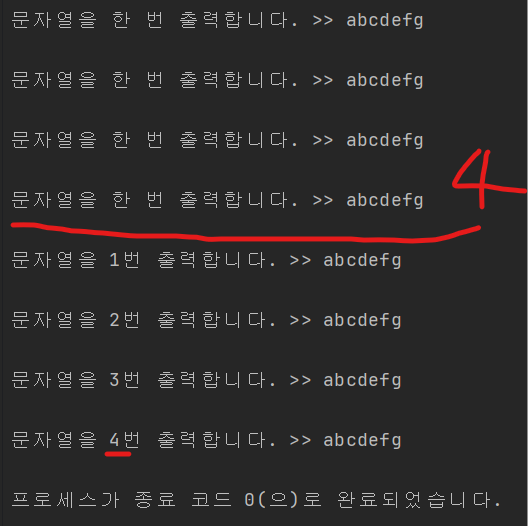
02.
// 책에 서술된 대로 구현
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct CandyBar
{
string maker;
double weight;
int calories;
};
void SetCandyBar(
CandyBar& candyBar,
const char* candyBarName = "Millennium Munch",
const double candyBarWeight = 2.85,
const int candyBarCalories = 350)
{
candyBar.maker = candyBarName;
candyBar.weight = candyBarWeight;
candyBar.calories = candyBarCalories;
}
void PrintCandyBar(const CandyBar& candyBar)
{
cout << "Candy Bar Info\n\n";
cout << "Maker: " << candyBar.maker << "\n";
cout << "Weight: " << candyBar.weight << "\n";
cout << "Calories: " << candyBar.calories << "\n";
}
int main()
{
CandyBar candyBar;
cout << "Default Candy Bar Info\n\n";
SetCandyBar(candyBar);
PrintCandyBar(candyBar);
cout << "\nSetting Candy Bar Info\n\n";
SetCandyBar(candyBar, "CandyCandy", 1.5, 300);
PrintCandyBar(candyBar);
return 0;
}결과
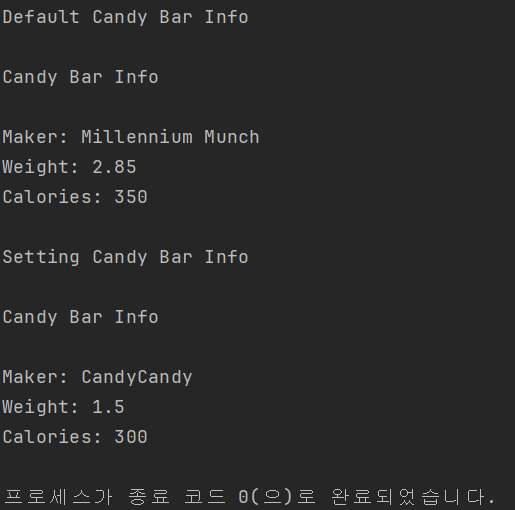
03.
// 책에 서술된 대로 구현
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void ToUpperCase(string& str)
{
for (char& c : str)
c = toupper(c);
}
int main()
{
cout << "문자열을 입력하시오 (끝내려면 q): ";
string str;
while (getline(cin, str) && str != "q")
{
ToUpperCase(str);
cout << str << '\n';
cout << "다음 문자열을 입력하시오 (끝내려면 q): ";
}
cout << "끝.";
return 0;
}결과

04.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
// 책에 서술된 대로 구현
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
struct stringy
{
char* str;
int ct; // 문자열의 길이 ('\0'은 제외)
};
void show(const stringy& sy, int n = 1)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << sy.str << '\n';
}
void show(const char* str, int n = 1)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << str << '\n';
}
void set(stringy& sy, char* str)
{
int len = strlen(str);
char* temp = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(temp, str);
sy.str = temp;
sy.ct = len;
}
int main()
{
stringy beany;
char testing[] = "Reality isn't what it used to be.";
set(beany, testing);
show(beany); // 문자열 멤버를 한 번 출력한다.
cout << endl;
show(beany, 2); // 문자열 멤버를 두 번 출력한다.
cout << endl;
testing[0] = 'D';
testing[1] = 'u';
show(testing); // testing 문자열을 한 번 출력한다.
cout << endl;
show(testing, 3); // testing 문자열을 세 번 출력한다.
cout << endl;
show("Done!");
return 0;
}결과
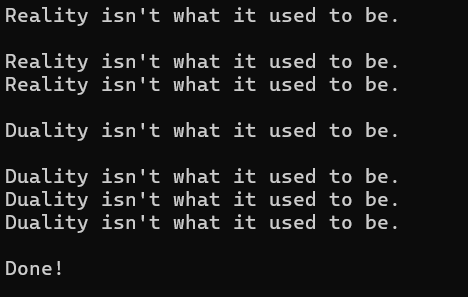
05.
// 책에 서술된 대로 구현
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 5;
template <typename T>
T max5(T arr[], int size)
{
T max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (max < arr[i])
max = arr[i];
}
return max;
}
int main()
{
int intArr[5] = {0, 3, 4, 109, 2};
double doubleArr[5] = {0.6, 4.3, 34.4, 1.09, 0.2};
cout << "최대값 찾기\n";
cout << "\nint 배열의 값: ";
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) cout << intArr[i] << " ";
cout << "\n최대값: " << max5(intArr, SIZE) << '\n';
cout << "\ndouble 배열의 값: ";
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) cout << doubleArr[i] << " ";
cout << "\n최대값: " << max5(doubleArr, SIZE) << '\n';
return 0;
}결과
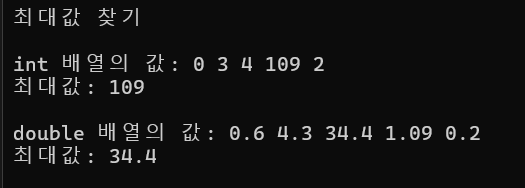
06.
// 책에 서술된 대로 구현
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
T maxn(T arr[], int size)
{
T max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (max < arr[i])
max = arr[i];
}
return max;
}
// 특수화
template <>
const char* maxn<const char*>(const char* arr[], int size)
{
const char* maxAddress = 0;
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (max < strlen(arr[i]))
{
max = strlen(arr[i]);
maxAddress = arr[i];
}
}
return maxAddress;
}
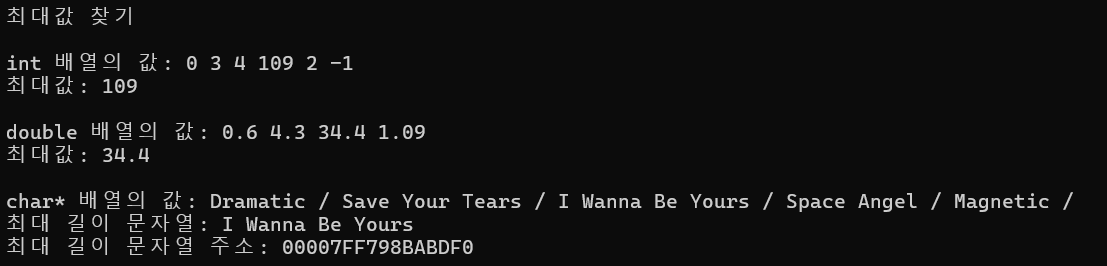
int main()
{
int intArr[6] = {0, 3, 4, 109, 2, -1};
double doubleArr[4] = {0.6, 4.3, 34.4, 1.09};
const char* charArr[5] =
{
"Dramatic",
"Save Your Tears",
"I Wanna Be Yours",
"Space Angel",
"Magnetic"
};
int intSize = sizeof(intArr) / sizeof(int);
cout << "최대값 찾기\n";
cout << "\nint 배열의 값: ";
for (int i = 0; i < intSize; i++) cout << intArr[i] << " ";
cout << "\n최대값: " << maxn(intArr, intSize) << '\n';
int doubleSize = sizeof(doubleArr) / sizeof(double);
cout << "\ndouble 배열의 값: ";
for (int i = 0; i < doubleSize; i++) cout << doubleArr[i] << " ";
cout << "\n최대값: " << maxn(doubleArr, doubleSize) << '\n';
int charSize = sizeof(charArr) / sizeof(char*);
cout << "\nchar* 배열의 값: ";
for (int i = 0; i < charSize; i++) cout << charArr[i] << " / ";
cout << "\n최대 길이 문자열: " << maxn(charArr, charSize) << '\n';
cout << "최대 길이 문자열 주소: " << static_cast<const void*>(maxn(charArr, charSize)) << '\n';
return 0;
}결과
07.
// tempover.cpp --- template overloading
#include <iostream>
template <typename T>
T SumArray(T* arr[], int n);
template <typename T>
T SumArray(T arr[], int n);
struct debts
{
char name[50];
double amount;
};
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int things[6] = { 13, 31, 103, 301, 310, 130 };
struct debts mr_E[3] =
{
{"Ima Wolfe", 2400.0},
{"Ura Foxe", 1300.0},
{"Iby Stout", 1800.0}
};
double* pd[3];
// set pointers to the amount members of the structures in mr_E
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
pd[i] = &mr_E[i].amount;
cout << "Listing Mr. E's 재산 목록 합계:\n";
// things is an array of int
cout << SumArray(things, 6) << '\n'; // uses template A
cout << "\nListing Mr. E's 채무 합계:\n";
// pd is an array of pointers to double
cout << SumArray(pd, 3) << '\n'; // uses template B (more specialized)
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
template <typename T>
T SumArray(T* arr[], int n)
{
using namespace std;
cout << "채무의 합계\n";
T sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += *arr[i];
return sum;
}
template <typename T>
T SumArray(T arr[], int n)
{
using namespace std;
cout << "재산 목록의 합계\n";
T sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
return sum;
}결과

'C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| next_permutation의 원리, 활용 (순열, 조합) (0) | 2025.02.16 |
|---|---|
| fill vs fill_n vs memset (0) | 2025.01.20 |
| friend 함수와 연산자 오버로딩 (0) | 2025.01.08 |
| [C++ 기초 플러스] Chapter 07 프로그래밍 연습 풀이 (1) | 2025.01.08 |
| 함수 원형은 왜 필요한가? (0) | 2025.01.08 |
